Arthritis
![]()
Call (703) 520-1031 or use the form to send us your contacts.
What Is Arthritis?
The general term of arthritis is used frequently to describe over one hundred types of joint pain or joint disease. People of all ages, sex, and race are affected by arthritis, with women being diagnosed more frequently than men are.
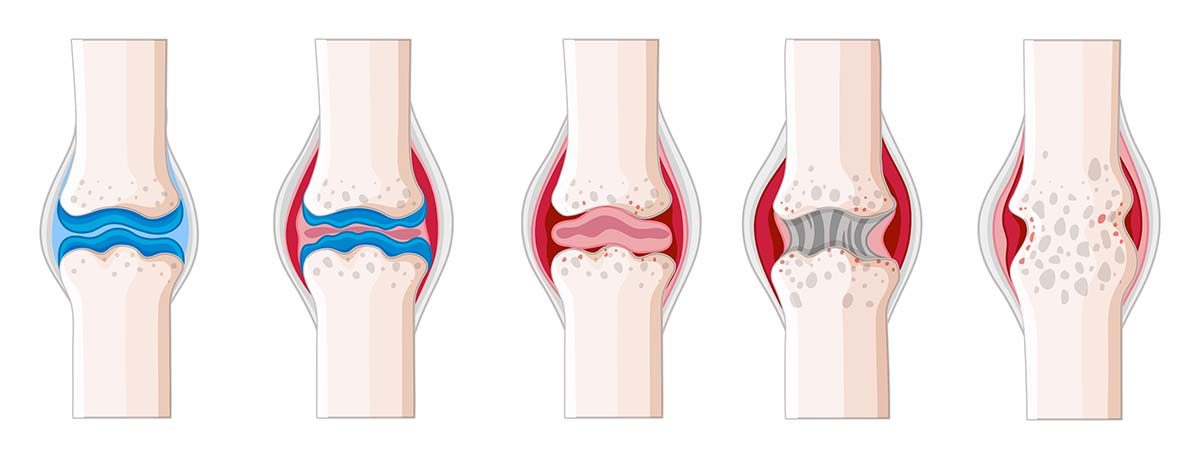
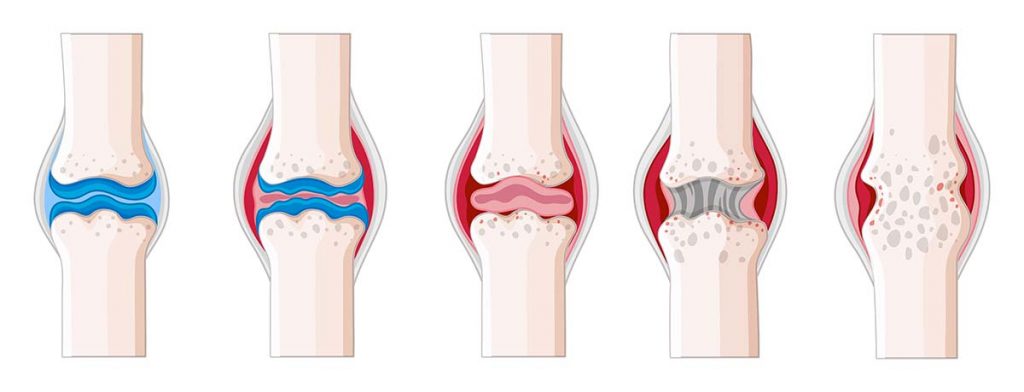
Osteoarthritis is the primary type of arthritis diagnosed, but other types are not so common. The wearing away of cartilage on the surface ends of the bones causes the inflammation and joint pain associated with arthritis. Mobility and fine motor activities become more difficult and painful. Arthritis can be infrequent in the beginning but can become more severe with time.
Arthritis Symptoms
There are many forms of arthritis; each includes specific symptoms and causes. The classic symptoms of arthritis are joint pain, swelling at the site of inflammation and loss of ability to perform functions such as walking up stairs and tying shoes with arthritis in hands. With some types of arthritis, there can be visible changes to the joints affected. Other types of arthritis require testing and examination to support a diagnosis.
What Causes Arthritis?
The causes of arthritis vary with each type. Each of the following forms of arthritis has a specific cause with joint pain and swelling being the common factor in most of the types:
- Metabolic arthritis is caused by high uric acid levels. Uric acid allows crystals to form in the joints causing pain and inflammation in the affected area. Gout is a term used to describe this form of arthritis.
- Inflammatory arthritis can be caused by genetic or environmental factors. Inflammation occurs due to the autoimmune system triggering a response. Included in this category are psoriatic and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Infectious arthritis is caused by a fungus, bacteria, or virus entering the system and is treated with antibiotics. Treatment is usually successful, but symptoms of arthritis may be chronic.
- Degenerative arthritis or osteoarthritis is the common form of arthritis. Causes of osteoarthritis are the wearing of bone cartilage, in turn, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling.
Diagnosing Arthritis
A diagnosis of arthritis is usually made initially with a primary care physician. The initial exam will include the following:
- A thorough medical history including past illness and a possible family history of arthritis.
- Physical examination especially of the joints and mobility.
- Lab and imaging tests will be ordered to determine the form of arthritis.
The primary physician may do all or most of the testing, or they may refer to a rheumatologist to complete the diagnosis.
Treating Arthritis
Rheumatologists encourage treating arthritis as early as possible. Treating arthritis in its early stages will stop further damage to the body. Drugs to treat arthritis have greatly improved, and treatment is successful when treated early. Preventing the damage to joints and affected parts of the body are successful in arthritis pain relief.
Arthritis FAQ
Can you make arthritis go away?
You can adopt behaviors that reduce their impact on your life. Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease, and medical research has not definitely proved what triggers it. Genetics are believed to be involved in making the body more susceptible to environmental factors. RA can go into remission, but arthritis does not go away.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative disease. Once it develops, the damage is done, but you can slow disease progression.
There are effective medical treatments today for both types of arthritis that can minimize the physical damage that rheumatoid arthritis can cause or prevent osteoarthritis from advancing. Lifestyle changes, like maintaining a healthy weight, are critical to managing arthritis in a way that enables you to resume normal activities.
What foods make arthritis worse?
Food cannot cure arthritis, but it can help make it more manageable. For rheumatoid arthritis, research has found that staying away from anti-inflammatory foods is wise and eating foods that lower inflammation and boost the immune system are best. The foods to avoid include salt, fried foods, processed foods, refined carbohydrates, refined sugar, and foods high in saturated fat.
The foods to avoid for osteoarthritis are the same as those for rheumatoid arthritis. The bottom line is a healthy well-balanced diet benefit the body, including the joints.
What does joint arthritis feel like?
Joint arthritis is a progressive disease. At first, there may be a dull ache in the joint, especially after using it for a period of time. It is recurring pain, unlike occasional pain associated with overuse. Joints may feel stiff at first with mild pain. In some cases, people experience joint pain in the morning which improves over a couple of hours after moving around.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an inflammatory disease, so joint pain is often accompanied by redness, swelling, and soreness in the joint. It usually attacks the joints on both sides of the body. Since RA impacts more than joints, you may also experience a general body ache and fatigue. Periods of inflammation come and go.
Osteoarthritis is also painful, especially after using the joint. The pain may or may not be noticeable in the morning but will worsen as the joint is used. There might be swelling, but it is likely due to irritated tissues in the joint. As the disease progresses, you may feel bones grating or the joint makes a popping sound.
If you are experiencing joint pain of any kind, the best thing to do is see a doctor for an evaluation. The sooner arthritis is managed, the more likely it can be controlled.
Is it possible to prevent arthritis?
There are situations in which arthritis cannot be prevented. This is especially true when arthritis develops has a genetic factor. However, taking care of your joints over a lifetime can either prevent osteoarthritis or at least slowdown disease progression of any type of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis.
For example, it is critical to maintaining a healthy weight because every 10 pounds of excess weight increases the force on knee joints by 30-60 pounds. Some of the positive behaviors to protect joints include getting regular exercise that does not create a high impact on the joints, following a well-balanced diet, lifting heaving items with a proper posture (protects the spine and hip/knee joints), carrying items held close to the body (protects wrists) and taking regular breaks from repetitive tasks. Always stay aware of the stress you are putting on joints no matter what you are doing.
How does arthritis affect the joints?
The two main types of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Though both affect the joints, they damage joints differently.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease involving the body’s immune system. The immune system attacks the synovial membrane which is the name for joint linings. If left untreated, eventually the lining, cartilage, and bone are destroyed. The typical symptoms are painful joint inflammation and swelling, to name two.
Osteoarthritis is referred to as a wear-and-tear disease. In this type of osteoarthritis, the cartilage that provides cushioning between joints deteriorates. Without the cushion, the bones grind together and eventually the connective joint tissues deteriorate. The typical symptoms of osteoarthritis are a pain when using the joint and restricted movement.